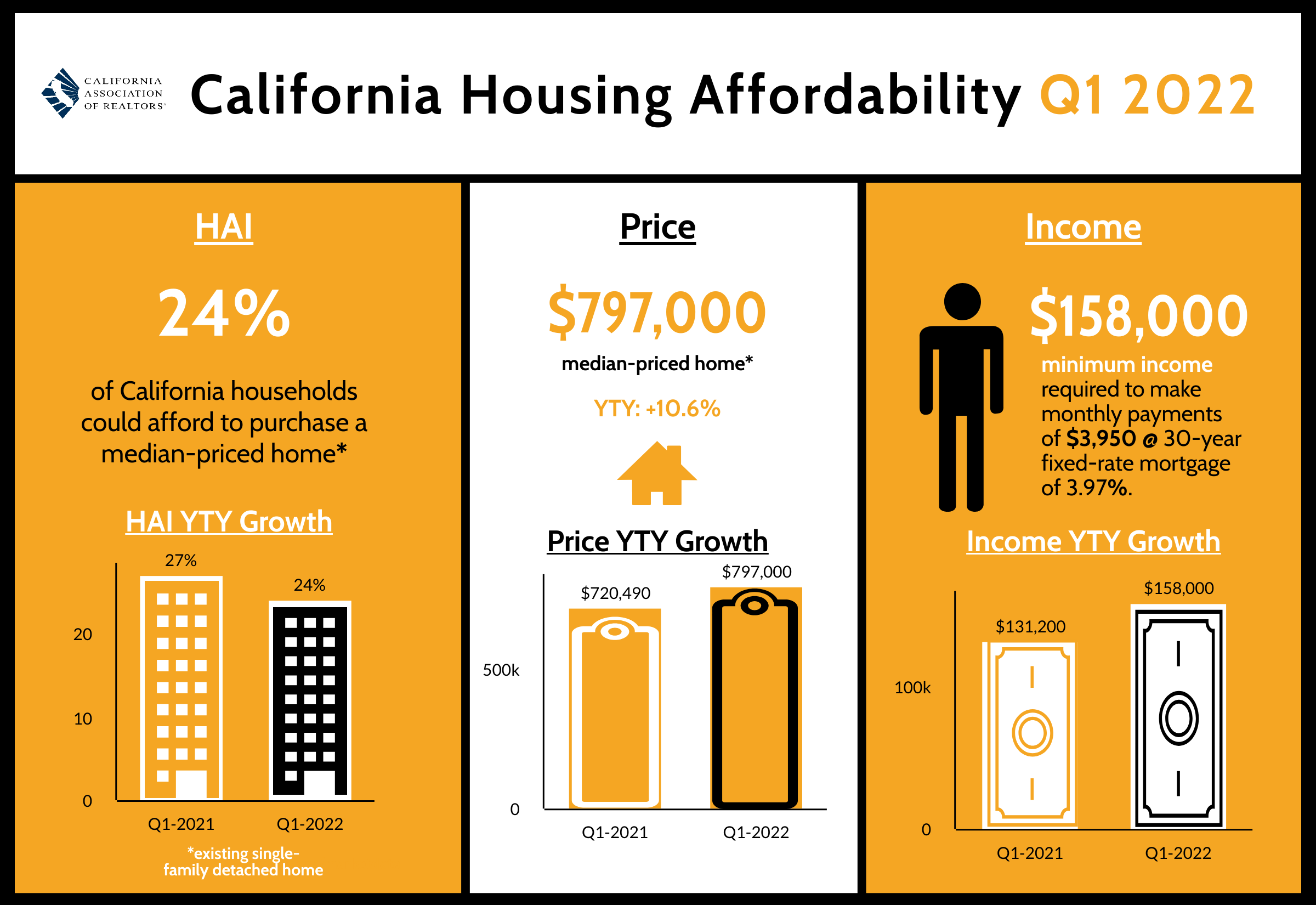
The percentage of home buyers who could afford to purchase a median-priced, existing single-family home in California in first-quarter 2022 ticked down to 24 percent from 25 percent in the fourth quarter of 2021 and was down from 27 percent in the first quarter of 2021, according to C.A.R.’s Traditional Housing Affordability Index (HAI). The first-quarter 2022 figure is less than half of the affordability index peak of 56 percent in the first quarter of 2012.
C.A.R.’s HAI measures the percentage of all households that can afford to purchase a median-priced, single-family home in California. C.A.R. also reports affordability indices for regions and select counties within the state. The index is considered the most fundamental measure of housing well-being for home buyers in the state.
A minimum annual income of $158,000 was needed to qualify for the purchase of a $797,000 statewide median-priced, existing single-family home in the first quarter of 2022. The monthly payment, including taxes and insurance on a 30-year, fixed-rate loan, would be $3,950, assuming a 20 percent down payment and an effective composite interest rate of 3.97 percent. The effective composite interest rate was 3.28 percent in fourth-quarter 2021 and 3.08 percent in first-quarter 2021.
With the median price of condominiums and townhomes reaching another record high in first-quarter 2022, affordability for condos and townhomes dropped from the previous quarter. Thirty-two percent of California households earned the minimum income to qualify for the purchase of a $640,000 median-priced condo/townhome in the first quarter of 2022, which required an annual income of $126,800 to make monthly payments of $3,170. The first quarter 2022 figure was down from 40 percent a year ago.
Compared with California, nearly half of the nation’s households could afford to purchase a $368,200 median-priced home, which required a minimum annual income of $73,200 to make monthly payments of $1,830. Nationwide affordability was down from 54 percent a year ago.